Chamberlain’s line, clivus-canal angle, Welcker’s basal angle, Boogaard’s angle, and foramen magnum angle: a brief review for type B basilar invagination
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37085/nsa.2024.6Keywords:
Basilar invagination, Skull base, Accuracy, Cephalometry, Diagnostic imagingAbstract
Introduction
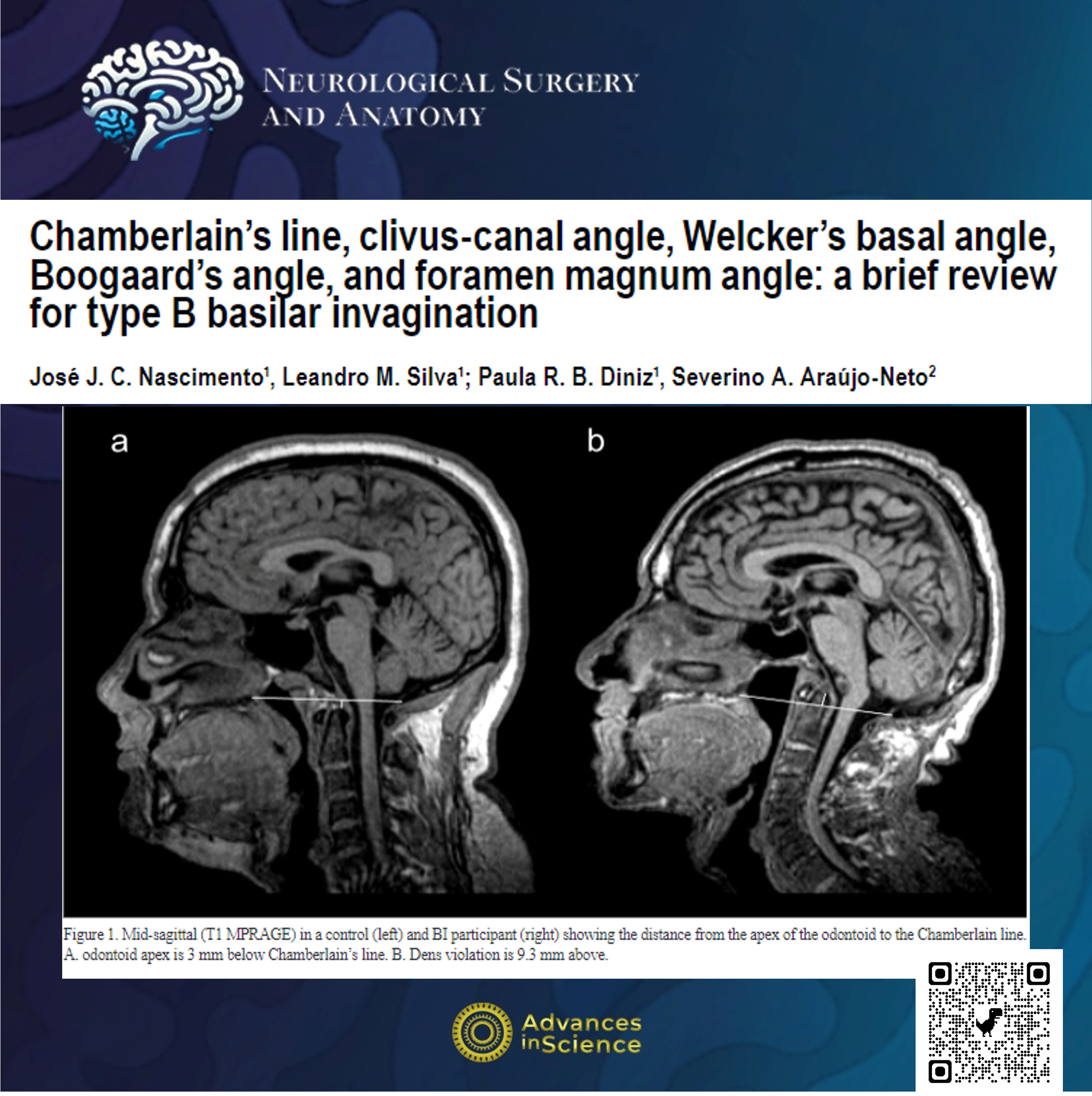
Type B basilar invagination (BI) is an abnormality of the craniovertebral junction (CVJ). Since first descriptions occurred in the 18th and 19th centuries BI have gained remarkable clinical and surgical importance.
Objective
To describe usual craniometric parameters of assessment of type B BI and to discuss future perspectives of craniometry in the field.
Methods
This is a brief review of the literature on the CVJ parameters used for the BI diagnosis.
Results
Although there are several craniometric parameters used in the diagnosis of BI, there are few studies on the validation of these parameters on radiography and volumetric images. Accuracy studies for Chamberlain’ line, clivus-canal angle, Boogaard’s angle, Welcker’s basal angle, and foramen magnum angle occurred consistently at CT and MRI. Brachycephaly and reduced cranial height are strongly associated with type B BI.
Conclusion
The classical parameters of the Chamberlain's line, Boogaard's angle and clivus-canal angle are still important tests for the diagnostic evaluation of type B BI.
References
- Shoja MM, Ramdhan R, Jensen CJ, Chern JJ, Oakes WJ, Tubbs RS. Embryology of the craniocervical junction and posterior cranial fossa, part I: Development of the upper vertebrae and skull. Clin Anat. 2018 May;31(4):466-487. Doi: 10.1002/ca.23049.
- Botelho RV, Botelho PB, Diniz JM. Where does the cranial base flexion take place in humans? An Acad Bras Cienc. 2020;92(1):e20190825. Doi: 10.1590/0001-3765202020190825.
- Botelho RV, Ferreira JA, Zandonadi Ferreira ED. Basilar Invagination: A Craniocervical Kyphosis. World Neurosurg. 2018;117:e180-e186. Doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2018.05.233.
- Nascimento JJC, Ribeiro ECO, Silva-Neto EJ, Araújo-Neto SA, Valença MM, Diniz PRB. Letter to the editor regarding "basilar invagination": It is not a single disease. Eur J Radiol. 2020 Nov;132:109280. Doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2020.109280.
- Silva JAG, Santos, AA, Melo LRS, Araújo AF, Regueira GP. Posterior fossa decompression with tonsillectomy in 104 cases of basilar impression, Chiari malformation and/or syringomyelia. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2011;69(5): 817-823.
- Chamberlain WE. Basilar impression (platybasis): a bizarre developmental anomaly of the occipital bone and upper cervical spine with striking and misleading neurologic manifestations. Yale J Biol Med. 1939; 11:487-496.
- Schuller A. Zur Röntgen-Diagnose der basalen Impression des Schadels. Wien. med. Wchnschr. 1911; 61: 2593-2599.
- De Vet, A. Basilar impresión of the skull. J Neurol Psychiatry. 1939; 3: 241- 250.
- Jain N, Ritu-Verma, Garga UC, Baruah BP, Jain SK, Bhaskar NS. CT and MR imaging of odontoid abnormalities: A pictorial review. Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2016;26:108-119.
- Smoker WR, Khanna G. Imaging the craniocervical junction.Childs Nerv Syst. 2008; 24:1123-45.
- Joaquim AF, Evangelista Santos Barcelos AC, Daniel JW, Botelho RV. Chamberlain's Line Violation in Basilar Invagination Patients Compared with Normal Subjects: A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2023 May;173:e364-e370. Doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2023.02.057.
- Nascimento JJC, Neto EJS, Mello-Junior CF, Valença MM, Araújo-Neto SA, Diniz PRB. Diagnostic accuracy of classical radiological measurements for basilar invagination of type B at MRI. Eur Spine J. 2019;28(2):345-352. Doi: 10.1007/s00586-018-5841-4.
- Xu S, Gong R. (2016) Clivodens Angle: a New Diagnostic Method for Basilar Invagination at Computed Tomography. Spine. 2016;41(17):1365-1371. Doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000001509.
- Henderson FC Sr, Henderson FC Jr, Wilson WA 4th, Mark AS, Koby M. Utility of the clivo-axial angle in assessing brainstem deformity: pilot study and literature review. Neurosurg Rev. 2018;41(1):149-163. Doi: 10.1007/s10143-017-0830-3.
- Henderson FC, Wilson WA, Mott S, Mark A, Schmidt K, Berry JK, Vaccaro A, Benzel E. Deformative stress associated with an abnormal clivo-axial angle: A finite element analysis. Surg Neurol Int. 2010;16;1:30. Doi: 10.4103/2152-7806.66461.
- Batista UC, Joaquim AF, Fernandes YB, Mathias RN, Ghizoni E, Tedeschi H. Computed tomography evaluation of the normal craniocervical junction craniometry in 100 asymptomatic patients. Neurosurg Focus. 2015;38(4):E5. Doi: 10.3171/2015.1.FOCUS14642.
- Frade HC, França CCNL, Nascimento JJCD, Holanda MMA, Silva EJD Neto, Araújo SA Neto. Cranio-vertebral transition assessment by magnetic resonance imaging in a sample of a northeast Brazilian population. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2017;75(7):419-423. Doi: 10.1590/0004-282X20170071.
- Boogaard, JA. De indrukking der grondrlakte van den schedel door de wervelkolom hare oorzaken en gevolgen. Nederlands Tijdschrift voor Geneekunde. 1865; 2: 81-108.
- Ferreira JA, Botelho RV. The odontoid process invagination in normal subjects, Chiari malformation and Basilar invagination patients: Pathophysiologic correlations with angular craniometry. Surg Neurol Int. 2015;8;6:118. Doi: 10.4103/2152-7806.160322.
- Alkoç OA, Songur A, Eser O, Toktas M, Gönül Y, Esi E, Haktanir A. Stereological and Morphometric Analysis of MRI Chiari Malformation Type-1. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2015;58(5):454-61. Doi: 10.3340/jkns.2015.58.5.454.
- Dufton JA, Habeeb SY, Heran MK, Mikulis DJ, Islam O. Posterior fossa measurements in patients with and without Chiari I malformation. Can J Neurol Sci. 2011;38(3):452-5. Doi: 10.1017/s0317167100011860.
- Peng L, Peng C, Yang F, Zuo W, Cheng C, Wang P, Zhang J, Li W. Comparative Analysis Between Machine Learning Algorithms and Conventional Regression in Predicting the Prognosis of Patients with Basilar Invagination: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Turk Neurosurg. 2023;33(4):665-675. Doi: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.36068-21.3.
- Nascimento JJC, Silva LM, Ribeiro ECO, Neto EJS, Araújo-Neto SA, Diniz PRB. Foramen Magnum Angle: A New Parameter for Basilar Invagination of Type B. World Neurosurg. 2021;152:121-123. Doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2021.06.028.
- de Oliveira Ribeiro EC, de Barros DPM, do Nascimento JJC, da Silva Neto EJ, de Araújo Neto SA, Valença MM. Anatomical Implications of Chiari I and Basilar Invagination (Type B) in the IV Ventricle and Cisterna Magna. World Neurosurg. 2023;178:e750-e757. Doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2023.07.154.
- Nascimento JJC, Carreiro NMF, Oliveira GT, Ribeiro ECO, Holanda MMA, Neto EJS, Araújo-Neto SA. Relationship between basilar invagination and brachycephaly in Northeastern Brazil. Eur J Radiol. 2018;104:58-63. Doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2018.05.006.
- Nascimento JJC, Silva LM, Ribeiro ECO, Neto EJS, Holanda MMA, Mello-Junior CF, Araújo-Neto SA, Diniz PRB. Investigating Type B Basilar Invagination Through Cephalic Indices. World Neurosurg. 2022;164:e1262-e1268. Doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2022.06.007.
- Botelho RV, Botelho PB, Hernandez B, Sales MB, Rotta JM. Association between Brachycephaly, Chiari Malformation, and Basilar Invagination. J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg. 2023;84(4):329-333. Doi: 10.1055/s-0041-1739503.
- Bossuyt PM, Reitsma JB, Bruns DE, Gatsonis CA, Glasziou PP, Irwig L, Lijmer JG, Moher D, Rennie D, de Vet HC, Kressel HY, Rifai N, Golub RM, Altman DG, Hooft L, Korevaar DA, Cohen JF; STARD Group. STARD 2015: an updated list of essential items for reporting diagnostic accuracy studies. BMJ. 2015; 28;351:h5527. Doi: 10.1136/bmj.h5527.